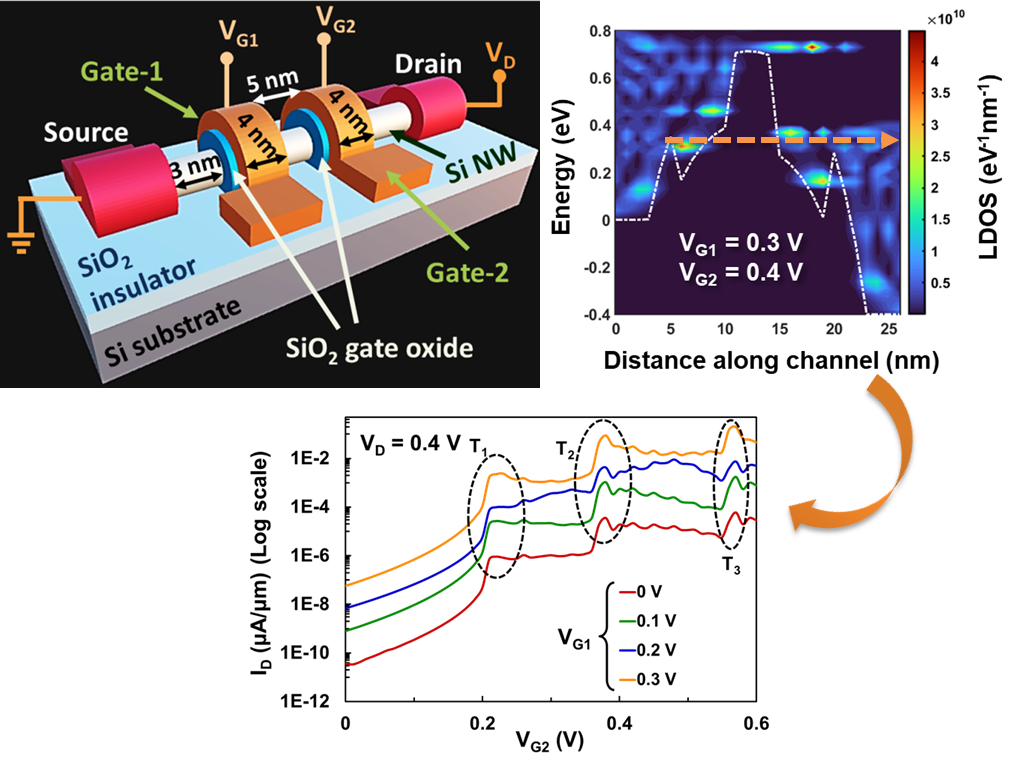
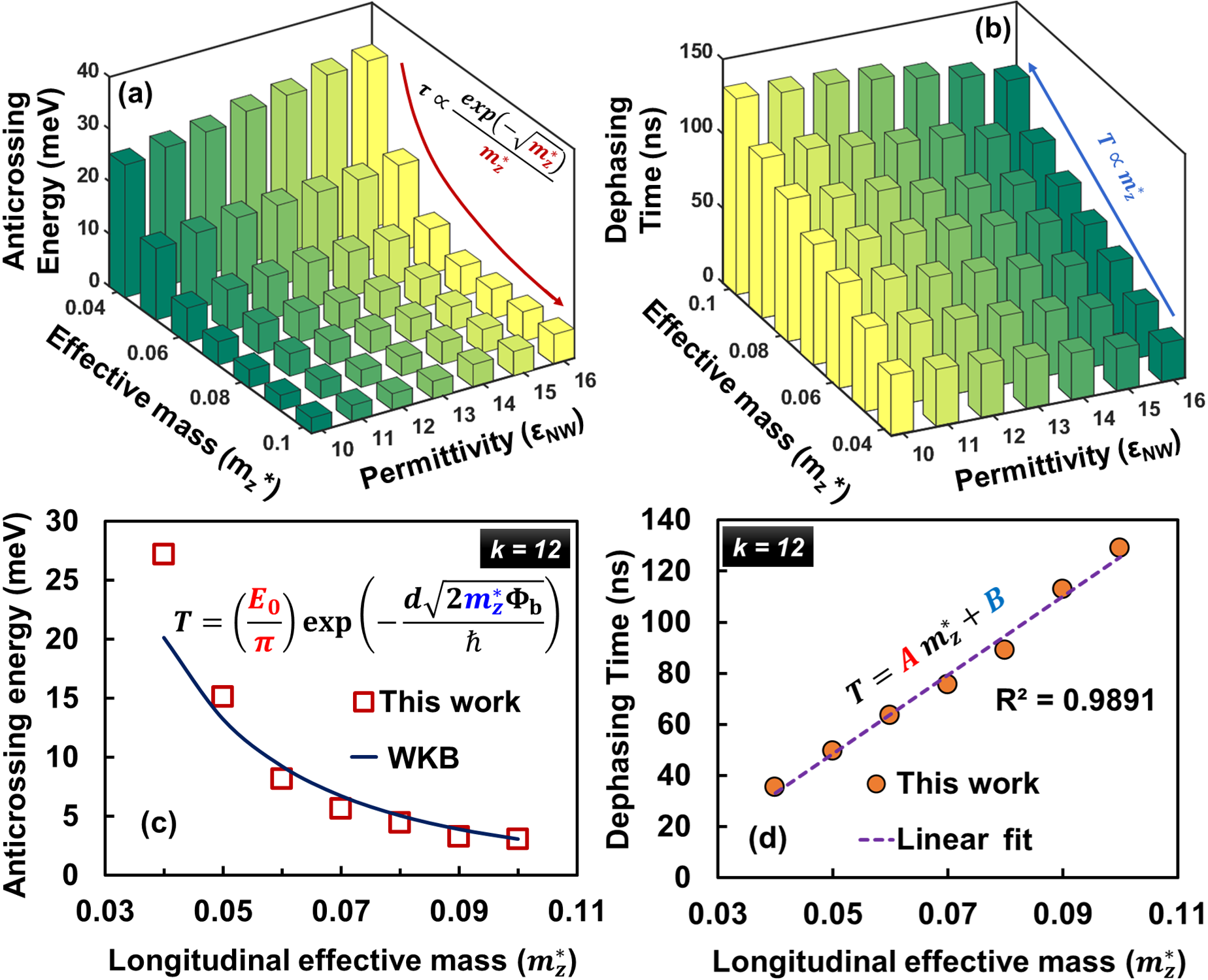
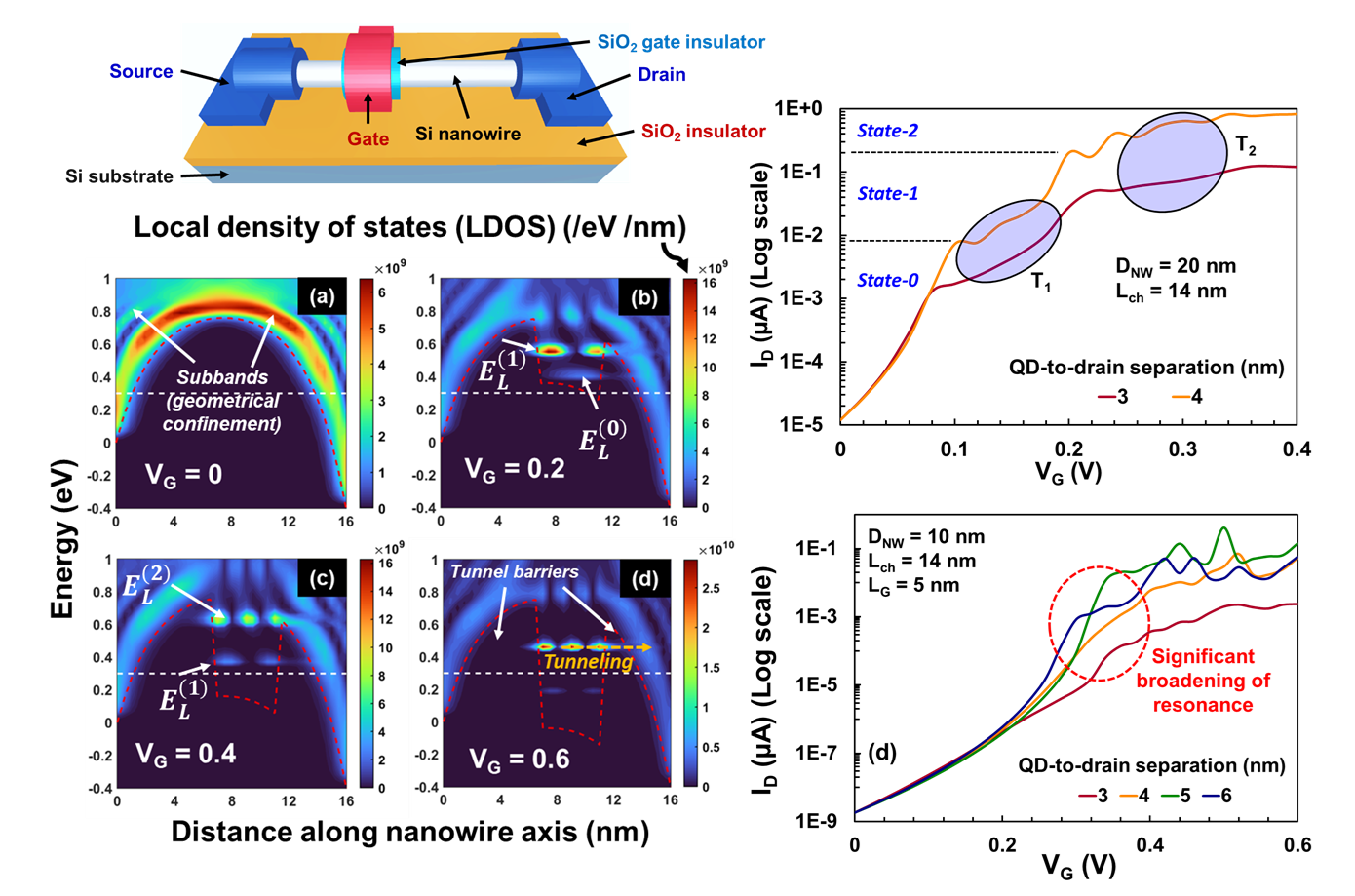
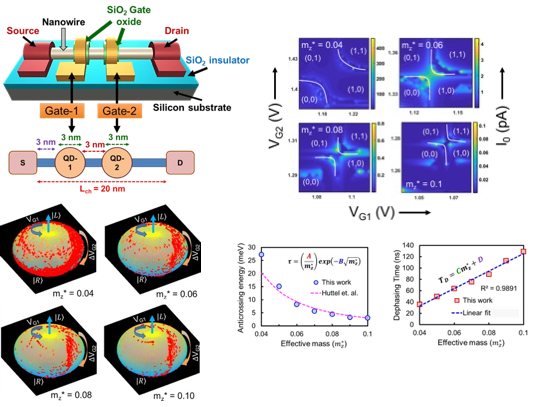
Exploring the Ga-doping dependent optical transparency and electrical conductivity of thermally evaporated p-type ZnO films
Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 36, 2304 (2025)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-025-16334-1
In this article, highly conductive p-type Ga-doped ZnO (GZO) films are thermally grown by engineering the oxygen interstitial (Oi) and zinc vacancy (VZn)-related intrinsic acceptor-type defects. Ga-doping controlled defect engineering approach in GZO films has been adopted for optimizing its optical transparency and electrical conductivity. The effects of Ga doping (0%, 2.5%, 5% and 7.5%) on the structural, morphological, compositional and optical properties of the films are systematically investigated by employing X-ray diffraction (XRD), Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and UV–Vis spectroscopy, respectively. Density functional theory (DFT)-calculations reveal Ga doping to significantly reduce the formation energies of oxygen interstitials and zinc vacancies. Electrical measurements confirm p-type conductivity in all of the doped samples. The 5% Ga-doped ZnO film provides the highest conductivity and figure of merit (F.O.M), and thus, suggesting it to be a promising p-type Transparent Conducting Oxide (TCO) for the future transparent electronic and optoelectronic applications.